What is VoIP: Voice over IP - how does it work
VoIP, Voice over Internet protocol is a form of telephone that uses internet technology to provide the connectivity between phones giving advantages of cost and flexibility.
Voice over IP, VoIP Includes:
VoIP basics
VoIP phones
How to choose best VoIP service provider
Understanding VoIP and how VoIP works can enable users of telephone services to make some cost savings as well as being able to take advantage of many improvements in facilities and flexibility that it provides.
Voice over Internet Protocol, also called Voice over IP or just VoIP is having a major impact on the telecommunications industry and not only gives advantages of cost, but also gives some significant advantages in terms of capability and flexibility.
Using VoIP technology, it is possible to carry both data and voice communications over the same network meaning that only one network is required for both.
VoIP was originally adopted by large enterprises, but the development of the technology and the associated reduced costs now mean that it is viable not only for large enterprise business telephone systems, but also for small businesses and even home environments.
As technology moves increasingly towards digital and Internet based techniques, and the costs falling, VoIP phone systems will only increase in their use.
What is VoIP?
The traditional method for domestic and business telephone systems was to use what is termed a circuit switched approach where dedicated lines take the phone signal to the switch or exchange where it is digitised.
With VoIP telephone systems the voice signal is digitised at the phone and sent as packet data using Internet Protocol. This makes far better use of the available network and providing greater flexibility whilst lowering the costs.
When using a VoIP telephone system, special VoIP phones are required. In essence, VoIP phones convert the voice signal to a digital or data signal in the form of data packets, and this is conveyed over the Internet network system in the same was as data for browsing, etc. If a traditional analogue phone needs to be used, then a converted box is required.
Accordingly VoIP can allow calls to be made over the Internet by computers etc, and applications like Skype and host of others are available for this. These offer the basic VoIP services, but may not allow connection to traditional landline or mobile services via the normal telephone network, i.e. where a number is dialled.
For phones that use a VoIP phone system installed in a business telephone system or as a domestic system, the special VoIP phones are required. These can connect to the data network in the business, making VoIP as a business phone system very attractive as only one network needs to be installed and maintained. These phones are typically connected so that they can
For small businesses and domestic residences, VoIP phones can also be an attractive option. VoIP phones themselves are more expensive than the traditional analogue ones, but they can provide some advantages.
VoIP phones often use Ethernet to connect to a network - they often connect to the router or wireless hub in a home situation, or some use USB and others can connect wirelessly.
In addition, wireless "hot spots" in locations such as airports, parks, and cafes allow connection to the Internet and may enable the use VoIP phone service wirelessly.
VoIP cost structures
As VoIP phone systems operate in a different way to that of traditional circuit switched analogue phone systems, the cost structures can be very different.
For applications like Skype where Skype to Skype calls are made there is no cost associated with the sale. Although if calls are made to a landline or mobile with a number over the telephone network, then there is a cost. Other similar applications use a similar model for charging.
For VoIP phones systems where special VoIP phones are used and a number allocated, there are a variety of different charging structures. This will depend on the particular telecommunications VoIP provider.
The traditional circuit switched charging structures tended to charge more for longer distance calls. The reasoning behind this was that longer stance calls utilised more circuits and therefore there was significant logic to this. With a VoIP phone system the situation is different and VoIP providers are starting to reflect this in their structures.
Some allow local calls free, others include country-wide calling, or state wide-calling in the basic cost plan. Other allow a certain number of minutes, etc. It is best to check on what the different available VoIP providers offer and make a decision based on the most cost effective operation for the given situation.
How does VoIP work
Digital technology is at the heart of VoIP phone systems and enables them to be used for business phone systems as well as for smaller installations as well.
VoIP definition:
VoIP (voice over IP) is the transmission of voice and multimedia content over Internet Protocol (IP) data networks. VoIP is enabled by a group of technologies and methodologies used to deliver voice communications over the internet, enterprise local area networks or wide area networks.
The concept of Voice over Interent Protocol, Voice over IP, or VoIP, is quite straightforward. A VoIP system basically consists of a number of endpoints which may be VoIP phones, mobile phones, VoIP enabled browsers on computers, etc and also an IP network over which the packet data is carried.
In a VoIP system, the phone or computer acting as an endpoint consists of a few blocks. It includes a vocoder (voice encoder / decoder) which converts the audio to and from the analogue format into a digital format. It also compresses the encoded audio, and in the reverse direction it decompresses the reconstituted audio. The data generated is split into packets in the required format by the network interface card which sends them with the relevant protocol into the outside world. Signalling and call control is also applied through this card so that calls may be set up, pulled down, and other actions may be undertaken.
The IP network accepts the packets and provides the medium over which they can be forwarded, routing them to their final destination.
Both ends of the communication will have distinct IP addresses and this enables the data packets to be correctly routed between the two phones.
As complete circuits are not dedicated to a single user as in the case of analogue circuit switched networks, at times when no data needs to be sent, for example during quiet periods in speech, etc, the capacity can be used by other users. This makes a significant difference to the efficiency of a system, and allows significant savings to be made.
Traditionally the term VoIP referred to systems where IP was used to connect private branch exchanges, PBXs, but now the term is more widely used and encompasses IP telephony.
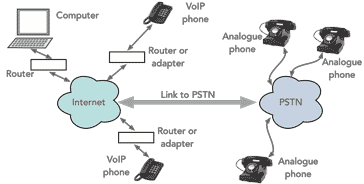
VoIP networks can take a variety of forms, so this just gives an ideal of what can be done
VoIP advantages & disadvantages
When considering a move to a VoIP telephone system, it is always worse to look at both sides of the case for the move. Whilst VoIP makes a lot of sense for a business telephone system, it can also have advantages for small enterprises and even domestic applications.
However there is never one ideal solution and the disadvantages must be considered along with the advantages.
VoIP advantages:
- One network system: For businesses one of the main advantages is the cost saving from only needing to instal one network system for computers / data. The business telephone system runs over the computer network, thereby only requiring one system to be installed and maintained.
- Can run on existing computers: Although many people and companies will want to maintain the use of a traditional telephone handset, it is also possible to completely move on from this approach and just use the computers that most people in an office use. A phone application can be run on the computer and this can be used with a headset or earphones with an attached microphone. Again this can provide cost savings in terms of hardware and maintenance.
- Mobility: With a VoIP telephone system it is far easier for people's numbers to follow them. As everything is run using software it is easy for the phones to 'move.' If the phone is run on a computer, simply logging in to one's account can allow the system to route calls correctly. This is ideal for offices where hot desking is used, or where people move around the country or even further.
- Improved efficiency: Using a packet switched network as int he case of VoIP increases the usage for the available capacity when compared to analogue circuit switched lines. This improvement in efficiency reduces overpaying costs and enables the telecommunications provider to offer a far more cost effective service.
- Cost: Cost can be a strong driver for many users. Providers can often give running costs that are well below those of traditional analogue systems, although this is sometimes as a result of the older systems having older pricing structures. However once installed there can be significant overall cost reductions, but check the offers and deals available and check both hardware and connection / call costs.
VoIP disadvantages:
- Lack of understanding of VoIP telephony: Many users and indeed many suppliers do not have a full understanding of VoIP telephone systems. This can mean that they are not always installed where they can provide the best service, or when they are installed, they may not be deployed in the most effective way.
- Emergency calls: In some areas and with some providers, emergency, 911, calls can be an issue. With traditional telephone systems, and with mobiles 911 (or whatever the emergency number is for the region) calls connect directly to the emergency services. This is not always the case with some VoIP providers. It is a point worth checking before proceeding if this could be an issue.
- Voice quality on poor connections: When using a VoIP telephone system over a poor broadband connection, be it via a smartphone, using a poor broadband line, or whatever, voice quality can be impaired. If data packets are lost as a result of them being timed out as a result of the poor connection, this will impact voice quality. This can be particularly apparent when using Wi-Fi or cellular connections where the network is congested as a result of high usage or the signal is poor and the data rate is very low.
- Different facilities: Although VoIP has been available for some time and is able to offer a lot more capability than analogue phones, there may still be some facilities that are different or not available. Normally any issues can be overcome, but there may be some issues with any migration.
In the long term VoIP is the way the market is moving, and now with increasing speed. Offering not only great improvements in flexibility, but also major cost savings, but with the requirement for large levels of investment, this is the way that the telecommunications market is moving. However to remain competitive it will be necessary to adopt the new VoIP technology.
Wireless & Wired Connectivity Topics:
Mobile Communications basics
2G GSM
3G UMTS
4G LTE
5G
Wi-Fi
Bluetooth
IEEE 802.15.4
DECT cordless phones
Networking fundamentals
What is the Cloud
Ethernet
Serial data
USB
LoRa
VoIP
SDN
NFV
SD-WAN
Return to Wireless & Wired Connectivity